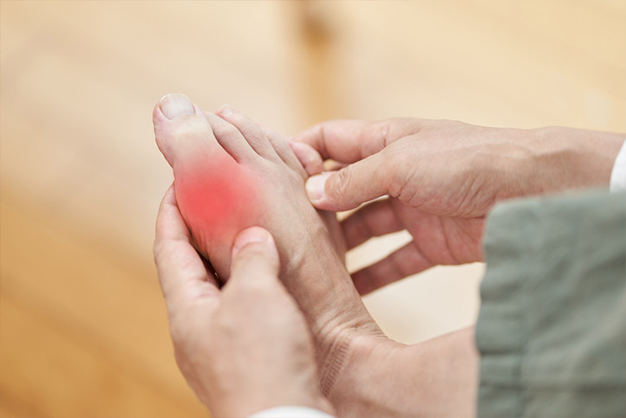
Introduction
Gout, often associated with excruciating pain and inflammation, is a form of arthritis caused by the buildup of uric acid crystals in the joints. With its roots in metabolic imbalance, gout requires a multifaceted approach for effective management. In this article, we will explore the causes, symptoms, and delve into the dietary strategies that play a pivotal role in controlling gout flare-ups.
Causes of Gout
Gout is primarily caused by hyperuricemia, a condition characterized by elevated levels of uric acid in the blood. Uric acid is a byproduct of the breakdown of purines, substances found in certain foods and naturally occurring in the body. When uric acid levels become too high, crystals can form in the joints, triggering painful gout attacks.
- Dietary Factors : Certain dietary choices can contribute to elevated uric acid levels and increase the risk of gout. Foods rich in purines, such as red meat, organ meats, seafood, and high-fructose corn syrup, may exacerbate gout symptoms.
- Genetics : Genetic factors can play a role in an individual's susceptibility to gout. Some people may have a genetic predisposition that makes them more prone to hyperuricemia and gout.
- Lifestyle Factors : Obesity, excessive alcohol consumption, and certain medical conditions, such as hypertension and kidney disease, can contribute to the development of gout.
Symptoms of Gout
Gout attacks typically manifest suddenly and are characterized by intense pain, swelling, and redness in the affected joint, often the big toe. The pain can be debilitating, making even the lightest touch excruciating. Gout attacks may subside on their own, but recurrent episodes can lead to chronic joint damage if left untreated.
Dietary Management of Gout
- Low-Purine Diet : Adopting a low-purine diet is a key component of managing gout. Foods to limit or avoid include organ meats, red meat, seafood, and high-purine vegetables like asparagus and mushrooms. Instead, focus on low-purine options such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and low-fat dairy products.
- Hydration : Staying well-hydrated is crucial for preventing gout attacks. Adequate hydration helps flush excess uric acid from the body, reducing the risk of crystal formation in the joints. Aim to drink plenty of water throughout the day.
- Limiting Alcohol : Alcohol, particularly beer and spirits, has been linked to an increased risk of gout. Limiting or avoiding alcohol consumption, especially during gout flare-ups, can help manage symptoms.
- Weight Management : Maintaining a healthy weight is essential for managing gout, as excess weight can contribute to elevated uric acid levels. Adopting a balanced diet and engaging in regular physical activity can support weight management efforts.
- Moderation and Balance : While it's important to limit certain foods, adopting a balanced and moderate approach is key. Instead of strict avoidance, moderation is encouraged. Incorporating a variety of nutrient-rich foods and maintaining a healthy lifestyle contributes to overall well-being and helps manage gout effectively.
Seeking Professional Guidance
Individuals with gout should work closely with healthcare professionals, including rheumatologists and dietitians, to develop personalized management plans. Medications to lower uric acid levels may be prescribed in addition to lifestyle modifications.
Conclusion
Understanding the causes, symptoms, and dietary management of gout is crucial for those affected by this painful condition. By adopting a holistic approach that combines dietary changes, hydration, and lifestyle modifications, individuals with gout can gain control over their symptoms and work towards preventing recurrent flare-ups. Seeking guidance from healthcare professionals ensures a comprehensive and personalized strategy for managing gout and improving overall joint health.
.pdf%20300X60%20PX-02-02.svg)