Author: Dr. Suresh Bhat, Senior Consultant, Urology
Understanding Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment Options
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) is a common non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland seen frequently in men as they age. It usually begins after the age of 50. Around 40-50% of men at age 50 and 80-90% of men by age 80 experience this condition. The most important point patients should understand is that BPH is not cancer, nor does it increase the risk of developing prostate cancer.
Why Does BPH Occur?
The exact cause of BPH is not clearly known. However, research suggests that hormonal imbalance, especially the reduction of the male hormone testosterone and the relative increase in estrogen, contributes to prostate gland growth.
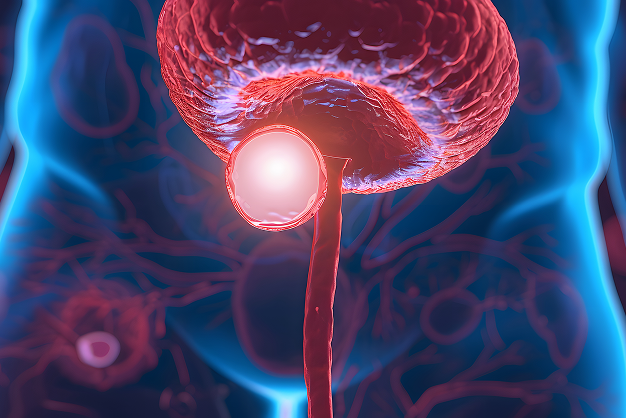
A normal prostate weighs around 20-30 grams. With age, it can grow to 50-60 grams, and in some cases even 100-200 grams.
The prostate is located below the bladder, and the urethra (urine tube) passes through it. When the gland enlarges, it compresses the urethra and obstructs urine flow, leading to various urinary symptoms.
Common Symptoms of BPH
Prostate size is not always directly related to symptom severity. Even mild enlargement can cause significant symptoms, while larger prostates may sometimes cause none. Typical symptoms include:
- Delay in starting urination
- Interrupted or weak urine flow
- Frequent nighttime urination (Nocturia)
- Sudden urge to urinate
- Urinary leakage
- Feeling of incomplete bladder emptying
- Dribbling at the end of urination
- Painful inability to urinate
- Blood in urine (Hematuria)
- Nighttime involuntary urination
Diagnosis and Evaluation
To diagnose BPH, the urology specialist may perform the following assessments:
- Medical history – Duration and severity of symptoms
- Physical examination – Including abdominal and genital examination, and Digital Rectal Examination (DRE)
- Urine test – To detect infection
- IPSS Score – To evaluate symptom severity
- Uroflowmetry – To assess urine flow rate
- PSA test – To rule out prostate cancer
- Ultrasound scan – To evaluate kidneys, bladder, prostate size, and residual urine
Consulting a qualified urologist in Kottayam or visiting a well-equipped urology department in Kottayam can ensure accurate diagnosis and expert care.
Treatment Options for BPH
1. Lifestyle Modifications (for Mild Symptoms)
Often, small changes can significantly improve symptoms:
- Limit daily water intake to about 2 liters
- Reduce water consumption after 8 PM
- Avoid caffeine and alcohol
- Exercise regularly
- Include more fruits and vegetables in your diet
- Prevent constipation
- Take allergy and pain medications cautiously
Possible Complications if Untreated
- Recurrent urinary infections
- Bladder stones
- Blood in urine
- Kidney damage or reduced kidney function
- Bladder muscle weakness
Surgical Options
Surgery is recommended when:
- Medicines fail to relieve symptoms
- Complications appear
- Severe symptoms affect daily life
Common Surgical Treatments
- TURP (Transurethral Resection of Prostate) – Gold standard
- Laser surgeries (Thulium, Holmium) – Ideal for high-risk patients
- Robotic surgery – Minimally invasive approach
- Open prostatectomy – For very large prostates
- Urethral lift – Preserves sexual function
- Prostatic artery embolization – Suitable for patients unfit for anesthesia
- Rezūm procedure – Uses water vapor; preserves sexual function
Living with BPH
BPH is a manageable condition that affects many men as they age. Early diagnosis, lifestyle changes, and appropriate treatment help maintain a healthy and comfortable life.
If you experience urinary symptoms, consult a urology doctor in Kottayam or the best urologist in Kottayam for expert evaluation. Caritas Hospital's urology department in Kottayam provides advanced diagnostics and comprehensive treatment for prostate-related conditions.
.pdf%20300X60%20PX-02-02.svg)