Author : Dr. Vysakha K. V
Consultant - Neurology & Movement Disorder, Caritas Hospital, Kottayam
What is Deep Brain Stimulation and who should consider it?
Deep brain stimulation is a surgical treatment PD, when the medical therapy alone fails to control the symptoms adequately. DBS is done in those PD patients who has an excellent response to the dopaminergic medication, but are experiencing the motor complications leading to decrement in quality of life. The main indications for DBS in PD are motor fluctuations with or without dyskinesias & drug refractory tremor. DBS is usually done in the intermediary stage of PD, where the patient has productive life and can reap maximum benefits of a quality of life. DBS very late in the disease, after the patient has memory problems, falls is not considered useful.
Will DBS be “Successful” ?
DBS can relieve the movement related symptoms of PD, including tremor, stiffness and slowness. Research has proven that the relief on an average can be 50-60%. DBS offers a stable control of baseline symptoms by providing 50% of what patients get with best ON ( with Levodopa) during all times. Depending on the extent of symptom control, a portion of the medication can also be reduced and thus relieving the “drug induced dyskinesias”. Both these factors help PD patient achieve a more stable and predictable symptom control with lesser complexity of medications. The question of “successful” DBS thus imply an improvement in the quality of life and to carry out their activities of daily living and improve the ability to return to work in some patients. This should be viewed with caution as symptoms seen late in the disease like imbalance, falls, freezing of gait etc may not respond to DBS. Similarly few of the non-motor symptoms like sleep dysfunction will improve with DBS, while memory issues, depression, anxiety psychosis may not respond to DBS.
How is the Deep Brain Stimulator system done?
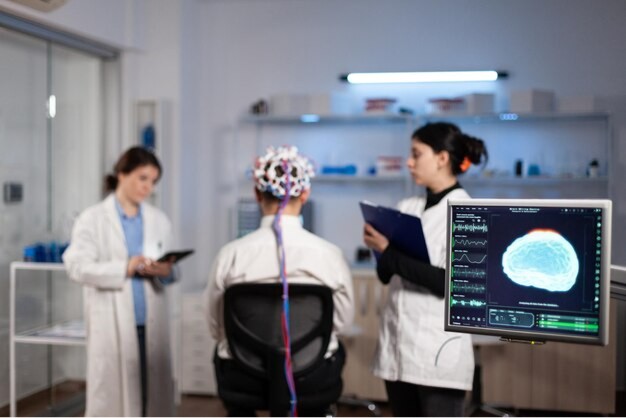
The DBS surgery has two steps. In the first step, a functional neurosurgeon trained in DBS will implant two electrodes in the brain with the help of a movement disorder neurologist trained in DBS. The first part of the surgery is done in awake stage in most patients, where the neurosurgeon implants two electrodes on either side at the pre-decided target after testing the patient intraoperatively for the relief of symptoms. During the second half of surgery, a pace maker(implantable pulse generator- IPG) similar to cardiac pacemaker is implanted on the chest wall which has a battery and programmable circuit and connected to the electrode tunnelling through the skin of neck. This part of surgery is done under general anaesthesia. Following the surgery, patient is shifted out of the theatre and monitored.
How does the machine start and when does the patient get the benefit?
Programming the IPG is done 7 days after the surgery. After screening the electrodes, a particular amount of current with its various parameters are determined by the neurologist, needed to relieve the symptoms are set. This process of identifying the ideal setting for an individual patient to relive his symptoms is called programming and done by the movement disorder specialist. Programming is done to ensure that the patient gets maximum control of the symptoms of PD at the cost of no or minimum adverse effects. The initial programming done may not give the best results, as surgery related factors (for example, swelling of the brain areas concerned, resulting from the trauma of the surgery) may interfere with it. The patient often requires re-programming a few weeks later for best therapeutic effects.
Are there complications for DBS surgery?
DBS is a neurosurgical procedure which has complications including bleeding inside the brain and infection of the implants, in a small minority of cases. The risk of serious bleeding resulting in paralysis is around 1.5 % ( 15 per 1000 DBS procedures).Infections in the implants (which may necessitate explantation of the DBS system) have been reported to occur in around 2-3% of the patients undergoing DBS all over the world.
Is the neurostimulator ( IPG) replaceable?
There are different types of neurostimulators including rechargeable ones. The service life will vary from 4-15 years depending on the type. When the neurostimulator reaches the end of its service life, it needs to be replaced. Replacing the neurostimulator is a minor surgical procedure and does not involve any brain surgery.
Are there other movement disorders in which DBS is used as treatment?
DBS is used for the treatment of other conditions like dystonia and various tremor disorders, including Essential Tremor.
.pdf%20300X60%20PX-02-02.svg)