Author: Dr. Avinash
OSA is a sleep-related breathing disorder. It is seen in many people globally. According to studies, this disease is seen in 20 -30% of the population globally.
Prevalence of OSA in India - Up to 13% in men, 5% in women.
OSA is a serious health problem, but the reality is that its severity often goes unrecognized.
1. What are the main symptoms of OSA?
- At night - Severe snoring, audible even in the next room
- Snoring suddenly stops, lying down without breathing for a while (partner says he noticed)
- Waking up suddenly at night without breathing
- Waking up to urinate frequently
- In the morning - Fatigue (all day)
- Headache, Dry throat, Sleeping all day Poor concentration, Memory loss or any Mental problems
2. What is the cause of OSA?
The basic problem of OSA is that the airways temporarily close during sleep. During REM sleep, the airways contract under the influence of nerves. When the muscles in the tongue relax, they move back, blocking the airways, resulting in a decrease in oxygen and an increase in CO2 in the blood. This stimulates the sympathetic nervous system, which also changes heart rate and blood pressure.
3. What are the risk factors for OSA?
- Old age (More common in men)
- Pregnancy
- Obesity (bmi 730kg /m2 )
- Alcohol
- Thyroid problem
- Enlarged tonsils/adenoids
- PCOD
4. What are the complications of OSA if left untreated?
- High blood pressure, Heart attack, Changes in heart rate (Arrhythmia), Stroke, Diabetes and any Mental health problems
Diagnosis
- Level 1 Sleep Study - Polysonography
- Evaluates breathing, heart rate, oxygen levels, movement, etc. during sleep
- HSAT - Home Sleep Apnea Testing - A home sleep study (Level 3, 4) is recommended for stable patients only
Treatment methods
- Lifestyle changes - Lose weight - Even a 10% weight loss can make a big difference in symptoms
- Avoid alcohol and smoking
- Sleeping on one side instead of lying down can slightly reduce snoring and the severity of the disease
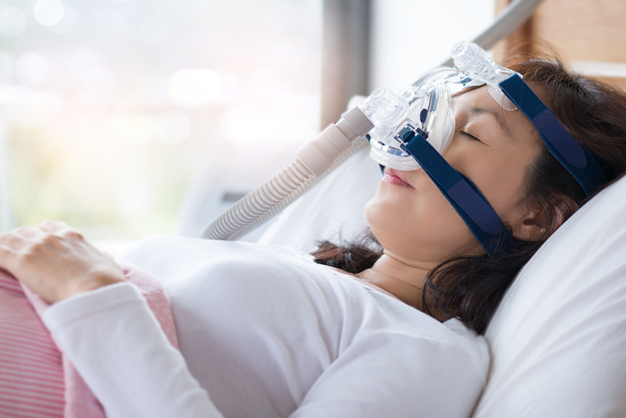
- CPAP (continuous positive airway pressure) - This is the most effective treatment for sleep apnea
- Oral appliances - Using devices prescribed by the dentist, the lower lip and upper lip are moved forward to reduce breathing difficulties
- Surgery - UPPP (Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty)
- Maxillo mandibular advancement - The chin is moved forward to enlarge the windpipe.
- Tracheostomy - Only done in severe cases
.pdf%20300X60%20PX-02-02.svg)