Introduction
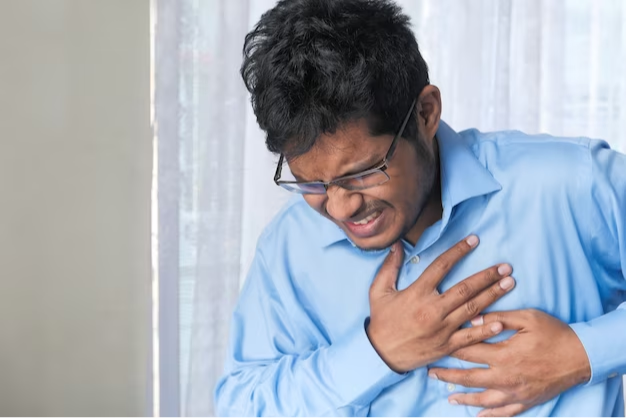
Heart disease is a leading cause of death for both men and women, but it often affects men differently due to unique risk factors. Understanding these risk factors and implementing prevention strategies is crucial for maintaining good heart health. In this article, we will explore the specific risk factors for heart disease in men and provide practical tips for prevention.
Risk Factors for Heart Disease in Men
- Age: As men age, the risk of heart disease increases, with most heart attacks occurring after age 65.
- Family History: A family history of heart disease, especially if it occurred at an early age, can raise a man's risk.
- High Blood Pressure: Hypertension is a significant risk factor for heart disease in men. Regular blood pressure monitoring and management are crucial.
- High Cholesterol:Elevated levels of LDL ("bad") cholesterol and reduced levels of HDL ("good") cholesterol can increase the risk of atherosclerosis and heart disease.
- Obesity: Excess weight, particularly around the abdomen, is a major risk factor. Maintaining a healthy weight is key.
- Smoking:Smoking is one of the most significant risk factors for heart disease in men. Quitting smoking can dramatically reduce this risk.
- Diabetes: Men with diabetes are at an increased risk of heart disease. Controlling blood sugar is essential.
- Physical Inactivity:A sedentary lifestyle can contribute to obesity and other risk factors. Regular physical activity is crucial.
- Diet: A diet high in saturated and trans fats, salt, and added sugars can contribute to heart disease. A heart-healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean protein is recommended.
- Excessive Alcohol Consumption: Drinking too much alcohol can increase blood pressure and contribute to obesity. Moderation is key.
Preventing Heart Disease in Men
- Regular Check-Ups: Schedule regular check-ups with a healthcare provider to monitor blood pressure, cholesterol levels, and other risk factors.
- Lifestyle Modification: Adopt a heart-healthy lifestyle by quitting smoking, maintaining a healthy weight, and staying physically active.
- Dietary Changes: Consume a balanced diet low in saturated fats, added sugars, and salt. Incorporate plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Exercise: Engage in regular physical activity, such as brisk walking, jogging, or other forms of aerobic exercise.
- Stress Management:Manage stress through techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises.
- Medication:In some cases, healthcare providers may recommend medication to control risk factors like high blood pressure or high cholesterol.
- Regular Health Screenings:Stay vigilant about regular health screenings, especially if you have a family history of heart disease or other risk factors.
- Social Support: Maintain strong social connections and rely on friends and family for support in making heart-healthy lifestyle changes.
Conclusion
Heart disease is a major concern for men, but it is not inevitable. Recognizing the unique risk factors and adopting prevention strategies is crucial for maintaining good heart health. By making lifestyle modifications, staying vigilant about risk factors, and seeking professional guidance when necessary, men can significantly reduce their risk of heart disease. It's never too late to take steps towards a healthier heart and a longer, more fulfilling life.
.pdf%20300X60%20PX-02-02.svg)