Introduction
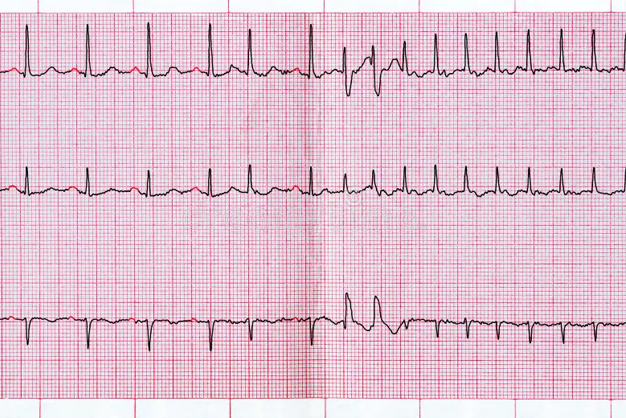
Atrial fibrillation, often referred to as AFib, is a common heart rhythm disorder that affects millions of people around the world. It occurs when the heart's upper chambers (atria) beat irregularly, leading to various symptoms and potential complications. In this article, we'll explore atrial fibrillation, its symptoms, the complications it can lead to, and the available treatment options.
Understanding Atrial Fibrillation
Atrial fibrillation is a heart condition characterized by irregular and rapid heartbeats. Normally, the heart's electrical system controls the rhythm and rate of heartbeats. In AFib, the electrical signals are disorganized, leading to chaotic and irregular heart rhythms. This can result in a decreased ability of the heart to pump blood effectively.
Symptoms of Atrial Fibrillation
- Palpitations : You may feel your heart racing, fluttering, or pounding.
- Fatigue : AFib can lead to reduced blood flow, causing tiredness and weakness.
- Dizziness or Lightheadedness : Insufficient blood supply to the brain can result in dizziness or fainting.
- Shortness of Breath : Difficulty breathing, especially during physical activity.
- Chest Pain or Discomfort : Some individuals experience chest pain or pressure.
- Confusion or Mental Fog : Reduced blood flow to the brain can lead to mental confusion or difficulty concentrating.
- CAD
- Vascular Heart Disease
Risk Factors :
Complications of Atrial Fibrillation
If left untreated, atrial fibrillation can lead to several serious complications, including :
- Stroke : Irregular heart rhythms can cause blood to pool in the atria, forming clots. If a clot dislodges and travels to the brain, block the flow of blood from arteries to brain
- Heart Failure : Prolonged AFib can weaken the heart, reducing its ability to pump blood efficiently, potentially leading to heart failure.
- Chronic Fatigue : The reduced blood flow can lead to persistent fatigue and a decreased quality of life.
Treatment Options for Atrial Fibrillation
The management of atrial fibrillation typically involves symptom control, prevention of complications, and efforts to restore and maintain normal heart rhythm & rate. Treatment options include :
- Medications : Your healthcare provider may prescribe medications to regulate your heart rate, control heart rhythm, and reduce the risk of blood clots.
- Cardioversion : This is a procedure that uses electrical shocks or medications to restore a normal heart rhythm in an acute state.
- Ablation Therapy : In cases where medications or cardioversion are ineffective, ablation procedures can be performed to destroy or isolate the abnormal heart tissue causing AFib.
- Blood Thinners : To prevent stroke, your doctor may recommend blood-thinning medications if you're at a high risk for clot formation.
- Lifestyle Modifications : Making lifestyle changes, such as reducing alcohol and caffeine consumption, managing stress, and adopting a heart-healthy diet, can help manage AFib.
- Implantable Devices : In some cases, a pacemaker or implantable cardioverter-defibrillator (ICD) may be recommended to help control heart rhythm.
Conclusion
Atrial fibrillation is a common heart condition that requires attention and management to prevent complications. If you experience symptoms of AFib or have been diagnosed with the condition, consult with a healthcare provider who can help determine the most suitable treatment plan for your specific situation. With proper management and lifestyle adjustments, many individuals with atrial fibrillation can lead healthy and fulfilling lives while minimizing the risks associated with this heart rhythm disorder.
.pdf%20300X60%20PX-02-02.svg)